Nature of Acids and Bases
Nature of Acids and Bases: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Common Element Present in All Acids, Conduction of Electricity in Acidic Solutions, Dilution of a Base with Water & Alkalies etc.
Important Questions on Nature of Acids and Bases
Give equations to show how the Phosphoric acid is made from its corresponding anhydride.
Name the acid present in vinegar. (Citric acid/Acetic acid)
Water insoluble bases such as , etc. are known as _____. (alkalis / non-alkalis)
The diagram of the apparatus given to show that the acid solution in water conducts electricity.
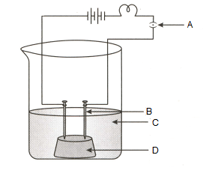
Identify the names of C and D from the given diagram:
Sort the acid, alkali and salt from the following:
(a) Lemon juice.
(b) Caustic soda.
(c) Slaked lime.
(d) Calcium Sulphate.
(e) Vinegar.
(f) Zinc Oxide.
(g) Salt.
(h) tamarind juice.
(i) Magnesium chloride.
The taste of acid is sour.
What is indicator? Give the names of any two indicators and what is the effect of acids and bases on them.
Metal ashes dissolve in water to form _____. (Base/Acid)
The taste of base is _____. (Sweet/Bitter)
Acids turn blue litmus paper to _____ .
Which one is the strongest acid amongst these -
Identify the hydronium ion among the following.
Name a tribasic Arrhenius acid.
Fill in the blank by using the correct words/terms given in the brackets.
A water-soluble base produces _____ ions in solution. (Hydrogen/Hydroxyl)
Strong acids readily donate protons than weak acid and strong base readily accepts protons than weak base.
The process of dilution of an acid or base in water is a highly exothermic one.
